1. (a) 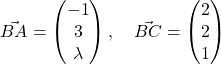
![]()
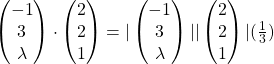
![]()
1. (b) ![]()
![]()
![]() is parallel to
is parallel to ![]()
![]() , where
, where ![]() is a scalar.
is a scalar.
![]()
![]()
![]()
2. Using partial fractions, we find that ![]()
![]()
Using method of differences (DIY), we have that
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
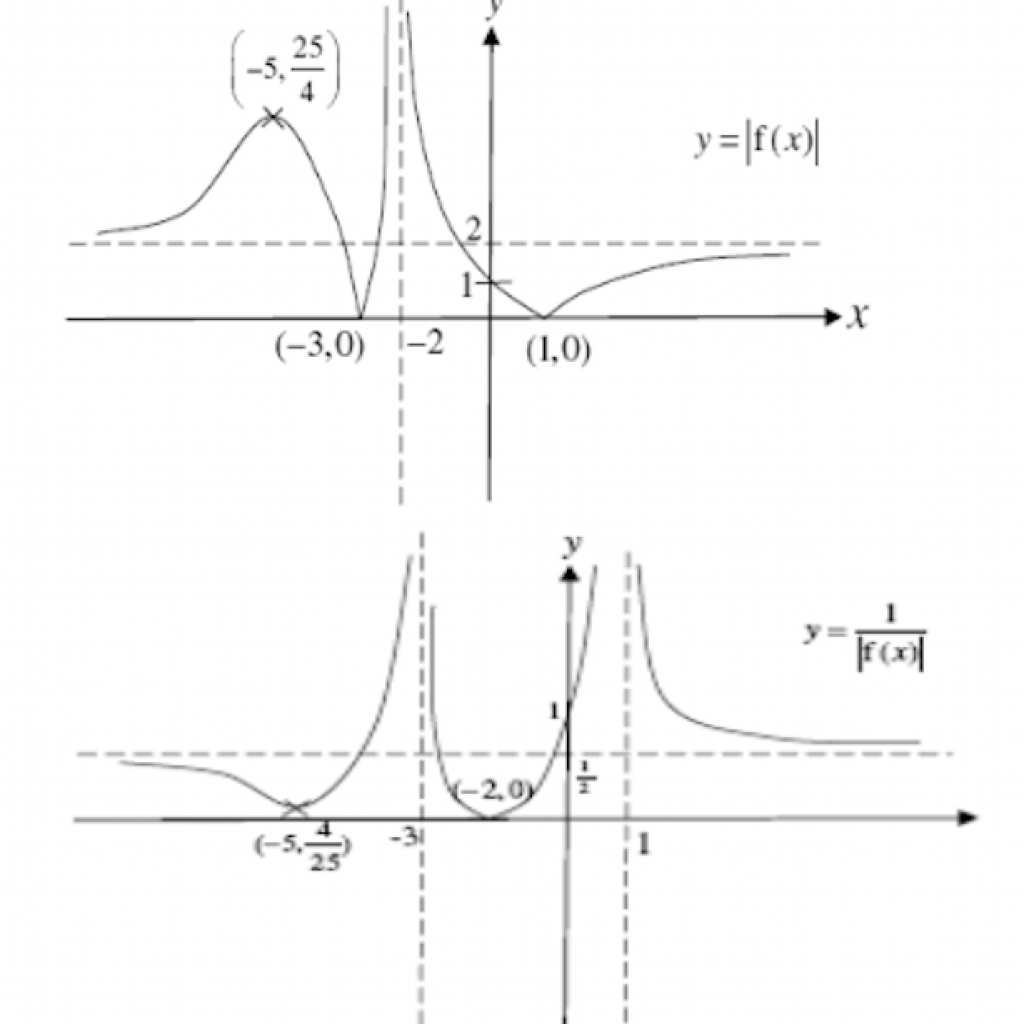
3. ![]() differs from
differs from ![]() by less than 1
by less than 1 ![]()
Plot the graph of ![]() and
and ![]() in the GC, sketch it out. * You can key in modulus by pressing (alpha)(window)(1).
in the GC, sketch it out. * You can key in modulus by pressing (alpha)(window)(1).
Observe that the ![]() -coordinates of the intersections points between the graphs are
-coordinates of the intersections points between the graphs are ![]() .
.
![]() .
.
4. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Replace ![]() with
with ![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
![]()
5. (i) ![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
5. (ii) Let ![]() , then
, then ![]() .
.
5. (iii) ![]()
![]()
![]()
6. (a) ![]()
Sum of first 40 even-numbered terms ![]()
We have ![]()
![]()
6. (b) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() years of extraction
years of extraction
7.
8. We substitute the given points ![]() and
and ![]() into
into ![]() . We have
. We have
![]() —(1)
—(1)
![]() —(2)
—(2)
![]() —(3)
—(3)
Using GC, ![]()
We have ![]() .
.
We observe we have a circle with centre ![]() and radius
and radius ![]()
9. (i) Equations of asymptotes: ![]() .
.
9. (ii) Max ![]() and Min
and Min ![]() . Axial intercepts:
. Axial intercepts: ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
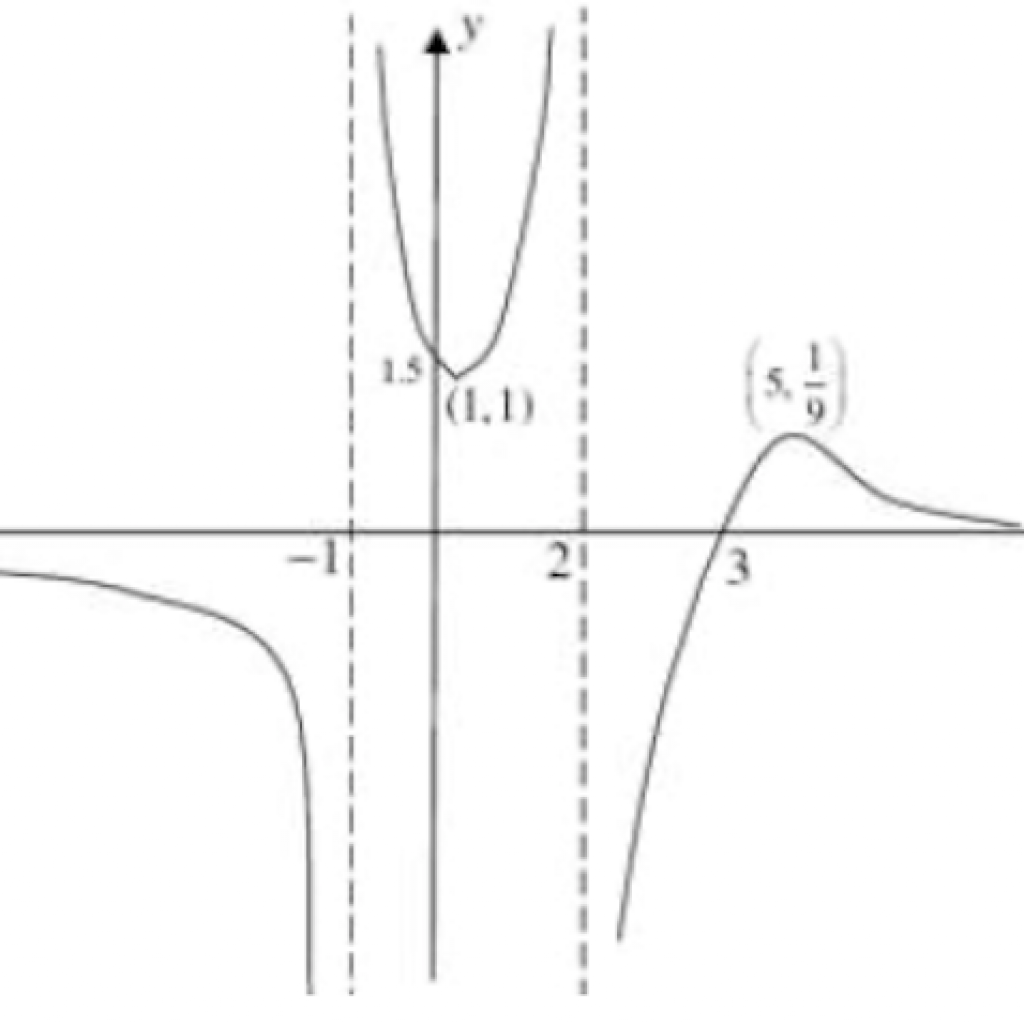
9. (iii) ![]()
(a) From the sketch, the line ![]() does not cut the curve when
does not cut the curve when ![]() .
.
(b) From the sketch, two real roots when ![]()
![]() .
.
10. ![]()


