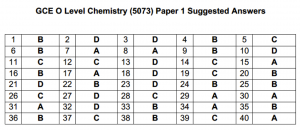
For those of you who just completed your GCE O Level Chemistry (5073) Paper 1, here are the suggested answers for the 40 MCQ questions. The paper was relatively straightforward so I hope that everyone is careful in answering the questions and you did not make careless mistakes. A good MCQ score is 38/40 if you want to ensure your A1.
The explanations to each question are as follow:
Question 1: B
A gas syringe is used to collect and measure the volume of the gas. The answer is not C because the graduated tube is only 50 cm3 which is insufficient to collect 80 cm3 of hydrogen gas produced in the reaction.
Question 2: D
Diesel and water are immiscible liquids so they need to be separated by using a separating funnel. The best answer for this question is D. Filtration cannot be used because it is used to separate an insoluble solid from a mixture while sublimation cannot be used because diesel and water cannot sublime.
Question 3: D
Acid reacts with a carbonate to release carbon dioxide gas (gas E). Ammonium salts reacts with an alkali to release ammonia gas (gas F). Acid reacts with an alkali to give a salt. Since ethanoic acid reacts with aqueous ammonia, the salt formed is ammonium ethanoate.
Question 4: B
The melting point of halogens increases down the group so bromine has a higher melting point than chlorine. Sodium is a solid while bromine is a liquid so sodium has a higher melting point than bromine. In general, metals have higher melting point than non-metals. Sodium has a lower melting point than diamond because it is a Group I metal and Group I metals have low melting point. Diamond has the highest melting point because it has a giant molecular structure with a network of strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms which require a large amount of energy to break. Hence, it has the highest melting point.
Question 5: C
The substance is an ionic compound. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling point and generally, most ionic compounds are soluble in water. They do not conduct electricity in solid state due to absence of free mobile ions as the ions can only vibrate and rotate about their fixed positions. However, they are able to conduct electricity when molten (liquid state) due to presence of free mobile ions.
Question 6: B
Bond formation is exothermic and hence, it releases energy. Electrolysis, fractional distillation and photosynthesis are endothermic reactions and hence, they absorb energy.
Question 7: A
Only the Cl atoms in CCl4 have the electronic configuration of 2.8.7. The rest of the atoms have the electronic configuration of 2.8.
Question 8: A
Metals conduct electricity due to the sea of free mobile electrons present in the giant metallic lattice structure. The positive ions present in the lattice are not mobile and cannot conduct electricity in solid state.
Question 9: B
In graphite, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms.
Question 10: D
The electronic configuration of oxygen atom is 2.6 so it will share 2 electrons in order to achieve stable electronic structure with full electron shells. The electronic configuration of fluorine atom is 2.7 so it will only share 1 electron. The electronic configuration of carbon atom is 2.4 so it will need to share 4 electrons.
Question 11: C
Oxygen gas exists as oxygen molecules (O2). Even in solid state as oxygen crystals, they will exist as oxygen molecules only.
Question 12: C
The electronic configuration of carbon is 2.4 while the electronic configuration of sulfur is 2.8.6. Hence, the carbon atom needs to share 4 electrons while each sulfur atom needs to share 2 electrons so that the carbon and sulfur atoms can achieve stable electronic structure with full electron shells. Each sulfur atom needs to form a double bond with the carbon atom.
Question 13: D
The number of moles for 1, 2 and 3 is 0.0500 mol. Since the limiting reagent is magnesium, magnesium oxide and magnesium carbonate for 1, 2 and 3 respectively, the number of moles of the product (magnesium sulfate) for 1, 2 and 3 would also be 0.0500 mol according to each of their equations:
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2
MgO + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2O
MgCO3 + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Question 14: C
X2 is a halogen because X exists as X– in the solution. When the electrolyte is concentrated aqueous sodium chloride, chlorine will be preferentially discharged at the anode.
Question 15: A
Mass of oxygen atoms in Y2O3 = 8.0 – 5.6 = 2.4 g
Number of moles of oxygen atoms in Y2O3 = 2.4 / 16
Number of moles of Y atoms in Y2O3 = 2.4 / 16 x 2 / 3
Question 16: B
Number of moles of ethanol = 23 / 46 = 0.500 mol
Number of moles of bromoethane obtained = 27 / 109 = 0.248 mol
Theoretical number of moles of bromoethane = 0.500 mol
Percentage yield = 0.248 / 0.500 x 100% = 49.6% ≈ 50%
Question 17: A
Electrode P is anode, electrode Q is cathode, electrode R is anode and electrode S is cathode.
Both the increases in mass of Q and S are due to the cations being discharged as solid at the cathodes.
Since the increase in mass of Q is greater than the increase in mass of S, the cation in cell 1 must be different from the cation in cell 2. Most likely, the cation in cell 1 is Ag+ and the cation in cell 2 is Cu2+.
Question 18: D
Metal X is copper since copper(II) carbonate is green and when it undergoes thermal decomposition, it produces copper(II) oxide which is black and carbon dioxide gas. Since the carbonate of metal Y did not decompose, Y must be a reactive metal such as sodium. Hence, metal X must be less reactive than metal Y (Statement 1 is wrong). All carbonates will react with dilute nitric acid to form carbon dioxide gas. Since metal X forms a coloured carbonate, it is most likely a transition element.
Question 19: C
The enthalpy change for the forward reaction is negative as it is exothermic. Hence, the enthalpy change for the reverse reaction is positive as it is endothermic.
Question 20: B
CO2, NO2 and SO2 are all gases at room temperature as they have a simple molecular structure with weak intermolecular forces of attraction between the molecules which requires a small amount of energy to overcome. Hence, they have low melting and boiling point. However, SiO2 is a solid at room temperature as it has a giant molecular structure with a network of strong covalent bonds between silicon and oxygen atoms which requires a large amount of energy to break. Hence, SiO2 has a high melting and boiling point.
Question 21: D
Neutralisation reaction is not a redox reaction. Hence, there is no change in the oxidation state of iron in iron(III) oxide when it reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Question 22: B
Limestone is added the Blast furnace to undergo decomposition to form calcium oxide to react with silicon dioxide present to form calcium silicate. The main impurity in the iron is carbon as carbon comes from excess coke that is added to the blast furnace. Calcium oxide is not normally added directly to the Blast furnace.
Question 23: D
NaHSO4 is an acid salt. From the equation given, NaHSO4 is able to dissociate in water to form hydrogen ions. Hence, the pH of NaHSO4 solution is less than 7. Barium nitrate solution will react with sodium sulfate to form a white precipitate of barium sulfate.
Question 24: B
When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to a solution containing Al3+ ions, a white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess aqueous sodium hydroxide, giving a colourless solution. However, when aqueous ammonia is added to a solution containing Al3+ ions, a white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess aqueous ammonia.
When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to a solution containing Zn2+ ions, a white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess aqueous sodium hydroxide, giving a colourless solution. When aqueous ammonia is added to a solution containing Zn2+ ions, a white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess aqueous ammonia, giving a colourless solution as well.
When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to a solution containing Ca2+ ions, a white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess aqueous sodium hydroxide. When aqueous ammonia is added to a solution containing Ca2+ ions, no visible reaction is observed. Hence, the solution remains colourless.
Question 25: B
A strong acid is an acid that dissociates completely in aqueous solutions to form a high concentration of hydrogen ions.
Question 26: C
X must be aluminium, lead or zinc.
Solid Y must be a non-metal since it cannot conduct electricity.
Z is a Group II metal as it forms an ionic oxide, ZO.
Z must be at the left hand side of the Periodic Table, while X is found in the middle of the Periodic Table and Y is on the right hand side of the Periodic Table.
Question 27: D
Solid astatine is black in colour as the colour intensity increases down the group for halogens.
Question 28: C
Transition metals have high densities.
Question 29: A
Brass is an alloy containing copper and zinc. Since both copper and zinc are metals, brass is able to conduct electricity. When brass reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, only zinc is able to react as zinc is more reactive than hydrogen in the reactivity series. Copper is below hydrogen in the reactivity series and is unable to react with the acid. Hence, the residue that is left behind is copper.
Question 30: A
In statement 1, Ar of G = [152 – (3 x 16)] / 2 = 52. Hence, G is chromium.
In statement 2, Ar of G = [160 – (3 x 16)] / 2 = 56. Hence, G is iron and iron will rust if both oxygen and water are present. Dry air does not contain water so iron will not corrode.
In statement 3, Ar of G = [102 – (3 x 16)] / 2 = 27. Hence, G is aluminium. Aluminium oxide is amphoteric as it can react with both acids and bases to form a soluble salt.
All 3 statements are correct.
Question 31: A
Since metal M is below copper in the reactivity series, metal M will also be below carbon and hydrogen in the reactivity series. Hence, carbon and hydrogen are able to displace M from its oxide to extract M.
Question 32: D
Air contains 78% of nitrogen gas. The first few tubes of oxygen collected will inevitably contain nitrogen gas.
Question 33: B
When ethene is converted to ethanol, the catalyst used should be phosphoric(V) acid. Using glucose, the conversion to ethanol should be carried at 37°C using yeast.
Question 34: A
The best answer is A because in simple terms, photosynthesis can be seen as the reverse of respiration. Option B is wrong because energy from sunlight is needed for photosynthesis, not respiration. Option C is wrong because respiration is carried out in both plants and animals. Option D is wrong because glucose is in solid state so “one volume of glucose” is wrong as it implies that glucose is in the gaseous state.
Question 35: B
From butane to methane, only flammability increases. The boiling point, melting point and viscosity decrease.
Question 36: B
The salt is calcium propanoate. Hence, the carboxylic acid is propanoic acid which comes from propanol (X) which contains 3 carbon atoms.
Question 37: C
The equation for the complete combustion of propane is:
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
Hence, 5 moles of oxygen are used.
Question 38: B
The fraction obtained at the top of the fractionating column should have the lowest boiling point.
Question 39: C
CxHy → 2C2H4 + 2C3H6 + C3H8
Hence, x = 13, y = 28
X contains 13 carbon atoms.
Question 40: A
The polymer is a protein, not nylon because the monomer contains both an amine group and a carboxylic acid group. The monomers for nylon will contain either both amine groups or both carboxylic acid groups at the ends. Hence, the best answer is that the polymer is a polyamide as it contains many amide linkages.

Hi, eagerly awaiting H1 suggested answers!
Hi, I was going through my TYS and was unsure for question 27. Why can’t 27 answer be B? Why won’t silver astatide be soluble in dilute nitric acid?
because we learnt that ionic compounds are soluble in water. And dilute nitric acid contains water. So wouldn’t it be soluble in it, or is that not how it works? O: