This page contains all questions and answers asked by students from this class. The most recent questions will be at the top.
…
Since the ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is a constant, the series convergences.
is a constant, the series convergences.
The sum to infinity ![]()
Let
Since they are consecutive terms of a GP,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Sum of first 3 terms
Sum of last 3 terms
Sum of n terms =
Solve for n.
(i) Volume,
Volume of kth later,
(ii)
Since
Theoretical Max Volume,
Total Volume,
We want

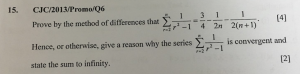



[…] Math Sat 130pm H2 Math Sat 330pm H2 Math Sun 930am H2 Math Sun 1130am H2 Math Sun 2pm H2 Math Mon 2pm H2 Math Mon 430pm H2 Math Mon 730pm H2 Math Tue 5pm H2 Math Tue 7pm H2 Math Thur […]