All solutions here are SUGGESTED. Mr. Teng will hold no liability for any errors. Comments are entirely personal opinions.
(i)
From GC, ![]() to 3 d.p.
to 3 d.p.
![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
Since ![]() ,
, ![]()
(ii)
Using the GC, ![]() to 3 d.p.
to 3 d.p.
(iii)
Area
![]()
![]()
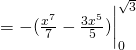
![]()
(iv)
![]()
Therefore, ![]() and f is an even function.
and f is an even function.
Since the coefficients of ![]() are all real, by conjugate root theorem, all complex roots occur in conjugate pairs. And since it is an even function, if
are all real, by conjugate root theorem, all complex roots occur in conjugate pairs. And since it is an even function, if ![]() is a root, then
is a root, then ![]() is also a root.
is also a root.
Thus, we have 2 real roots, ![]() and 4 complex roots,
and 4 complex roots, ![]() , where
, where ![]()
Personal Comments
Since the question asks for 3 d.p., its a hint that you can use your GC. Students should not waste further time. For (ii), some students went further to modulus the answer, citing that area cannot be negative. This shows poor understanding of the question as they simply want the integral evaluated and we are not looking for any area here. So yes, a definite integral can be negative in value but an area cannot. (iii) is looking for area, so we diligently modulus our answer.
The last part is a staggering 4 marks and I like subtle this question is, combining integration with complex numbers. This question can easily tell us who are the top students and study H2 Mathematics as a whole.

[…] 1: Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 Question 9 Question 10 Question […]